Foundation: Types, Use, Objectives
Foundations
Definition & Introduction
Foundation are structural elements, which transfer loads to the soil from columns, walls or lateral loads from earth retaining structures.
A structure essentially consists of two parts, namely the super structure which is above the plinth level and the substructure which is below the plinth level. Substructure is otherwise known as the foundation and this forms the base for any structure. Generally about 30% of the total construction cost is spent on the foundation.The soil on which the foundation rests is called the “foundation soil”.Shallow FootingDeep Foundation
Types of Foundation
The two main types of foundation are :
- Shallow foundation/Footings
- Deep foundation
Shallow Foundation
Shallow Foundation are usually located no more than 6 ft below the lowest finished floor OR Depth (D) of foundation is less than or equal to its width (B). When the soil bearing capacity of soil upto low depth is sufficient to take the structure load then it is provided.

Shallow Footing
Types of Shallow foundation
- Isolated spread footing
- Combined footing
- Cantilever or strap footings
- Wall footings
- Raft or Mat foundation


Use of Shallow Foundation
A shallow foundation system generally used when
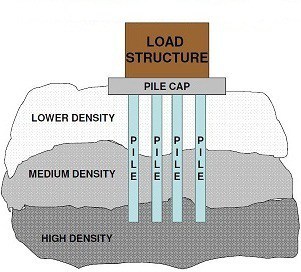
- The soil close the ground surface has sufficient bearing capacity
- Underlying weaker strata do not result in undue settlement. The shallow foundations are commonly used most economical foundation systems.

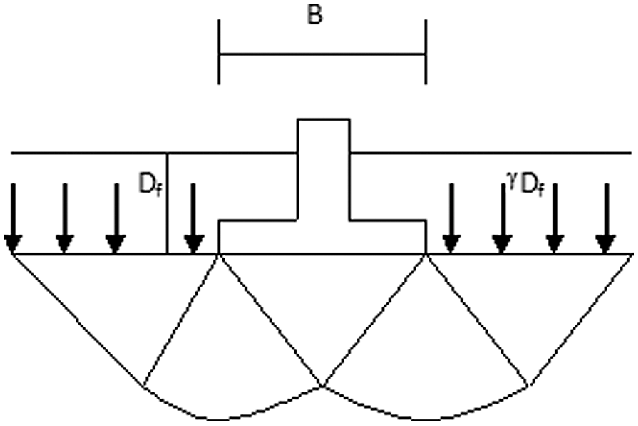
Deep Foundations
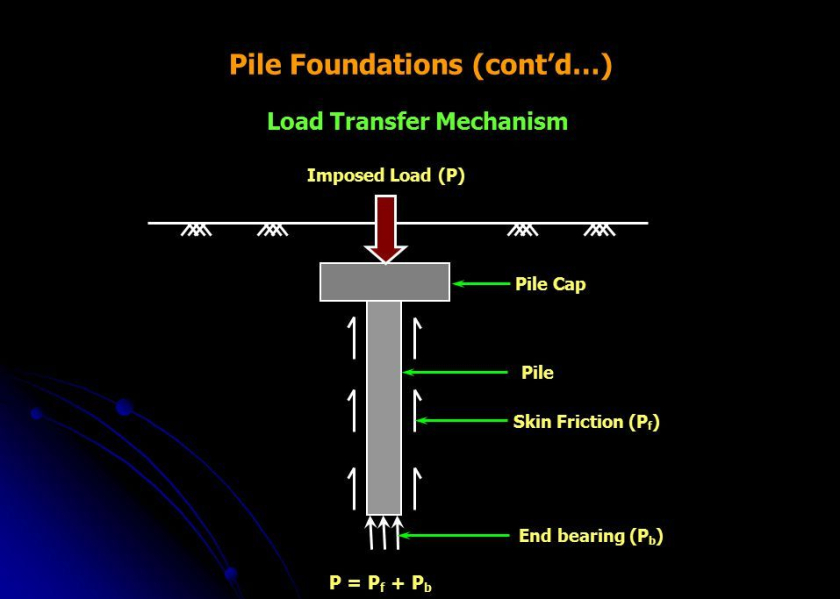
The shallow foundations may not be economical or even possible when the soil bearing capacity near the surface is too low. In those cases deep foundations are used to transfer loads to a stronger layer, which may be located at a significant depth below the ground surface. The load is transferred through skin friction and end bearing.Deep Foundation
Types of Deep foundation
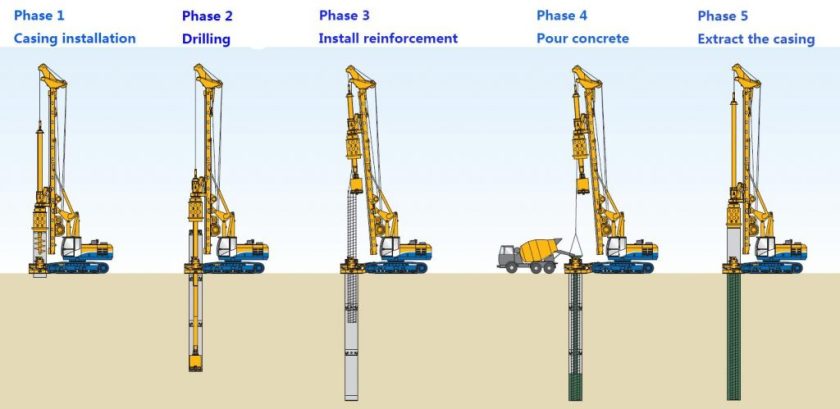
- Pile foundation
- Pier foundation
- Types of Pile foundation :
- Friction pile
- Load bearing pile

Objectives of a foundation
- To distribute the total load coming on the structure on a larger area.
- To support the structures.
- To give enough stability to the structures against various disturbing
- forces, such as wind and rain.
- To prepare a level surface for concreting and masonry work.